Investment Readiness
Question?
Do you know why startup fails in the investment stage?
Why is a great team with immense potentials not funded by Angels or VC Funds?
Why are entrepreneurs always frightened lest their ideas are not stolen by the big shark?
What you MUST KNOW!
Find what your investors search in your business before they invest!
How you can make your company lucrative to your investors!
How you can protect your million dollar idea!
Key Seven Elements of Investment Readiness
- Team, Talent, Advisor
- Product & Market
- Technology & Operation
- Tractions, Revenue & Growth
- Financial & Performance Management
- Legal Compliance & Admin
- Fundraising
How you can Protect your business IDEA
Your Asset as a Startup Company
- Copyrighted Software, content & product model
- Patented Innovation or Design
- Market Reach with Traction
- Your Brand Image
Tip 12: Build for quality and scale
Your product must be built with quality and scale in mind.For that, you should be using version control to track changes, doing unit tests and code reviews for quality control. Also, you should have a contingency plan for disasters and make sure you don’t lose client data.
In order to grow, your product needs to be built on a platform that can scale. The most common problems for a scalable platform are:
• The Response Time – the time taken to process request and return response
• Capacity Planning – figuring out the required infrastructure
• Architecture Bottlenecks such as:
• A centralised component in the application architecture which can not be scaled out, adds an upper limit
• A latency component is a slow component that puts lower limit on response time
Tip 13: Know the different acquisition channels and find yours
Poor marketing is the #7 reason startups fail. Marketing is just the “top of funnel” elements of awareness and acquisition, but it is the starting point of the startup’s growth and indispensable.
Some acquisition channels scale, some don’t. Generally, you start with things that don’t scale well. Try both inbound (longer setup but longer payback) and outbound (instant.)

Also, you need to decide if you should be spending on acquisition (and growth).
Follow this rule:
• Searching for Product/Market Fit, conserve cash;
• Searching for a Repeatable & Scalable Sales Model: spend experimentally;
• Scaling the business: spend aggressively
Tip 14: Know how to measure and find product/market fit
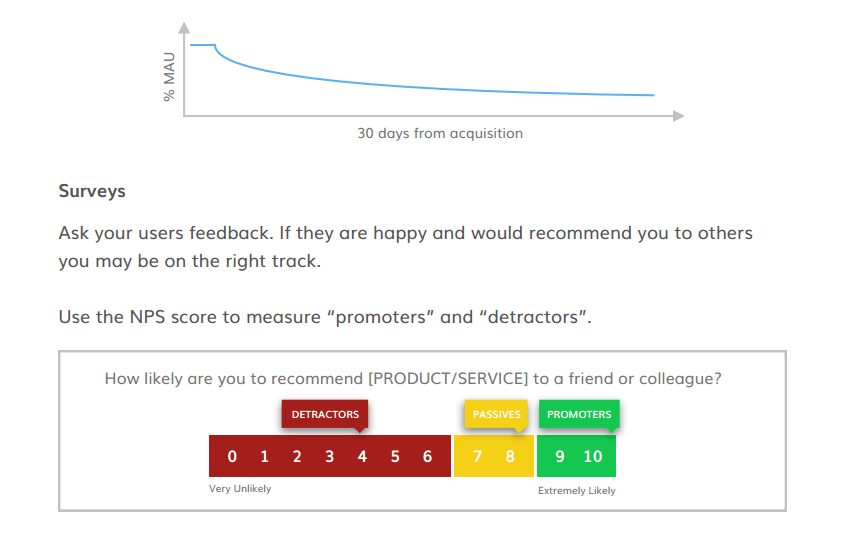
There are various methods to help you determine if you have product/market fit. It’s related to the #1 reason startups fail “No market need”. If your customers don’t get value from your startup’s product or service, why would they hang around?
So, does your retention flatten out? If so, you may be retaining enough users for a viable business.
Gut Feeling
What do your instincts tell you?
Are customers buying as fast as you can make it? Media/reporters are calling you? Can hire fast enough? Money is piling up?
OR
Is it forced? Are sales cycles long / deals never close?
Tip 15: Know and measure your unit economics
Knowing your unit economics will be critical when you are in front of sophisticated investors, but they are also metrics that will help you run a better business.
To measure your unit economics, there are some formulas that help you:
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): ($) Total sales and marketing expenses / (#) new customers acquired LTV to CAC Ratio Calculation: ($) LTV / ($) CAC
Lifetime value (LTV)
Churn: [ (#) Total customers churned this time period / (#) Total customers at the start of this time period ] x 100 = (%) Customer Churn Rate
• For SaaS companies:
⁃ ($) Average monthly revenue per customer x (# months) customer
lifetime x Gross Margin (%)
⁃ ($) Average monthly revenue per customer x (1 /monthly churn) X
Gross Margin (%)
• For Ecommerce companies:
⁃ ($) Average Order Value x (#) Repeat Sales x (# months) Average
Retention Time x Gross Margin (%)
• For Mobile Apps (note that adding the referral value is optional):
⁃ ($) Average revenue per user x (1/monthly churn) + ($) Referral
value x Gross Margin (%) = ($)
LTV to CAC Ratio Calculation: ($) LTV / ($) CAC
The most important aspect is that if your LTV to CAC ratio is at least 3, otherwise your ratio is too low. You should always aim for it to be higher than 3.
Page 1 Page 2 Page 3 Page 4 Page 5
Are you curious to know what are the available fund raising platform for the startups?
Do you know what are the 30 legal services that a startup might need to carry on their new business?
